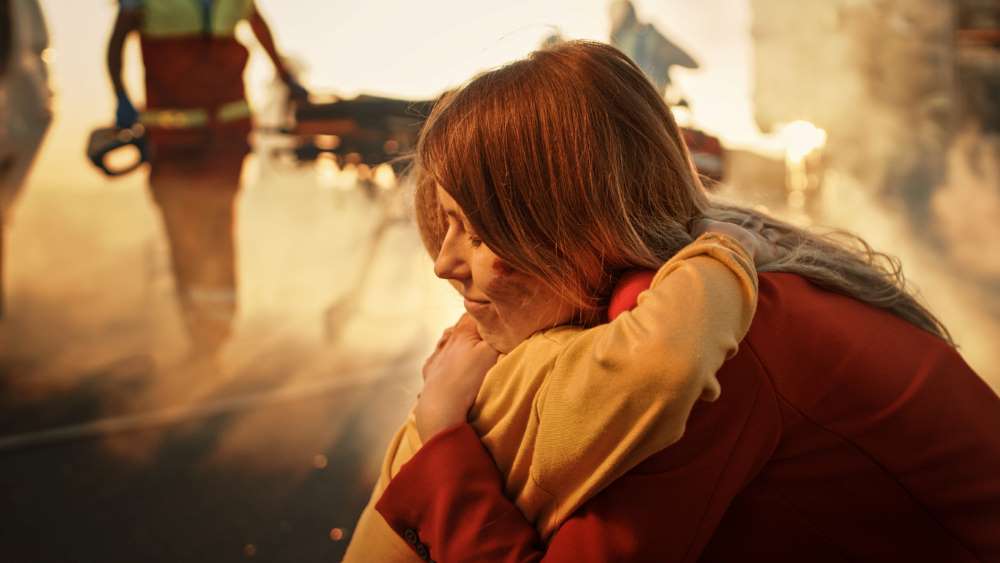
“Half the time I cry into a pillow because the stress is overwhelming.”
These were the words of a 12-year-old boy who survived a car accident with his family.
While driving on holiday, his dad struggled to control the trailer containing the family’s camping equipment. As the car went out of the control, it veered onto the shoulder. When the father tried to straighten up back onto the highway, he drove straight into the side of a pickup truck causing his vehicle to bounce back onto the shoulder and crash into a mailbox. The vehicle rolled over multiple times causing a major accident.
The family was airlifted to the nearest hospital. Sadly, mom and dad didn’t make it.
Miraculously, all six children survived leaving them without parents.
Children who lose their attachment figures or receive serious injuries in car wrecks face emotional health consequences that can persist throughout adulthood.
Every child should live a carefree existence with parents devoting every waking hour to ensuring this. Dangerous events such as car wrecks still happen beyond a parent’s control.
Childhood Traumatic Stress
Unfortunately, childhood trauma can cause reactions to life events long after the traumatic event is over.
Such drastic events in a child’s life can cause powerful physical and emotional reactions. A child may feel fear, helplessness, terror, and physiologically react with loss of bladder control, vomiting, or heart pounding.
Childhood traumatic stress can have a range of symptoms including:
-
Depression
-
Anxiety
-
Intense emotional upset
-
Difficulty focusing
-
Problems with developing relationships
-
Nightmares
-
Insomnia
-
Aches and pains
-
Academic difficulties
As a traumatized child grows older, they may engage in risky sexual behavior, crime, or start taking drugs.
Reminders and Adverse Life Events
Memories of the traumatic event can trigger these emotional and physical symptoms in children. Everyone experiences negative memories of some kind, but children with traumatic stress experience more dramatic reactions.
Children who survive car accidents may have sudden drastic life changes such as moving home, living with new caregivers, a change in school, or living with an injury, pain, or disability.
Certain events will trigger memories of the traumatic event, which can ripple through whole families, friendship groups, schools, and even whole communities.
How Traumatic Stress Affects Children in Later Life
Children who have suffered a traumatic event are more likely to develop post-traumatic stress disorder or complex post-traumatic stress disorder. Complex post-traumatic stress disorder refers to multiple stressful events.
A child who has been in a serious car accident may experience further trauma as a consequence of the accident, such as losing a loved one.
According to the American Psychiatric Association, there are four main types of symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder including:
-
Intrusion
-
Avoidance
-
Changes in cognition or mood
-
Alterations in arousal and reactivity
Intrusion
Intrusion refers to flashbacks, nightmares, thoughts, and feelings about the traumatic event. Flashbacks can be so vivid that a person may feel as though they are reliving the event.
Avoidance
A person with post-traumatic stress disorder may try to suppress memories of the event as they are too painful. This might mean resisting talking about their feelings or any detail about the event. Avoiding memories may typically mean avoiding people, places, and situations that remind them of the event.
Changes in Cognition or Mood
Post-traumatic stress may cause a person to develop disproportionate self-beliefs arising from the event. A person may start to believe they are to blame for the event, resulting in unhealthy negative thought patterns and a loss of enjoyment in activities.
Alterations in Arousal and Activity
Irritability, suspicion, angry outbursts, self-destructive behavior, difficulty sleeping, or concentrating are just a few ways that post-traumatic stress disorder can manifest in a person.
The knock-on effects of these behavioral changes will impact a person’s relationships with others and make life difficult in work relationships.
Research shows that many adults who experience childhood trauma go on to self-medicate with alcohol and drugs to avoid confronting difficult emotions. A child must get the right course of psychiatric treatment to decrease the likelihood of developing a substance use disorder.
Treatment of Childhood Traumatic Stress
Around 25% of road accident victims develop post-traumatic stress disorder, which means timely treatment is vital to prevent worsening psychological symptoms.
The National Child Traumatic Stress Network (NCTSN) has centered around the US dedicated to healing childhood trauma with evidence-based interventions.
According to the NCTSN, the trick is to get in early. A child goes through trauma screening and a trauma-informed mental health assessment to gain a detailed understanding of their condition.
As childhood trauma is complex the NCTSN has developed numerous avenues of treatment. Each child will have unique circumstances and experience a different type of trauma.
After assessment treatment may include any of the following modalities depending on the severity and type of trauma a child experiences including:
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy for families
-
Attachment and biobehavioral catch-up
-
Attachment, self-regulation, and competence
-
Child and parent psychotherapy
-
Child and family stress intervention
-
Early pathways
-
Family-centered treatment
-
Integrative treatment of complex trauma for children
-
Risk reduction through family therapy
These are just a few modalities offered to children with traumatic stress. All of these interventions are designed to help a child to address and confront their trauma and equip them with healthy coping strategies.
Does Your Child Have Traumatic Stress After an Accident?
If your child has experienced a car accident they could be suffering from traumatic stress. It’s advisable to seek professional medical help if they display any of the following symptoms:
Preschool Children
-
Nightmares
-
Screaming or crying
-
Poor eating habits
-
Fear of leaving parents or caregivers
Elementary School Children
-
Anxiety or fear
-
Difficulty concentrating
-
Inability to sleep
-
Feelings of guilt or shame
Middle/High School Children
-
Depression
-
Social withdrawal
-
Eating disorders
-
Self-harm
-
Alcohol or drug abuse
What To Do If Your Child Has Traumatic Stress
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) advises that parents and caregivers play an important role in managing childhood trauma.
To support a child with trauma SAMHSA suggests the following:
-
Reassurance: Remind the child that they are safe and explain how you will ensure they will stay safe at home and school. It’s normal for a child to feel guilt and blame themselves for the accident. Keep assuring the child that they are not to blame.
-
Show patience: It may take a long time for a child to heal from the experience. Keep supporting them emotionally and remind them that they are not responsible for what has happened.
More information on how to manage a childhood with trauma can be found here and remember to keep your kids safe in the car at all costs.